Introduction
Abu Dhabi Global Market (ADGM) and Dubai International Financial Centre (DIFC) are both free financial zones in the UAE, with their own independent legal jurisdiction that is independent from the UAE Civil Commercial Law. Entrepreneurs often stand out in front of both attractive options for opening their new business, without knowing what is more suitable for accomplishing their goals, this is why this blog will help you understand the major differences between DIFC vs ADGM and choose the more suitable for your business.
Launched in 2004, DIFC was established under the vision of His Highness Sheikh Mohammed bin Rashid Al Maktoum, and transformed in the past 20 years to become a powerful global financial center. Which made it a home for more than 60% of GCC FinTech companies in by 2022.
ADGM was introduced in 2013, as part of Abu Dhabi’s economic diversification plans. Since its operation, it “gained international recognition for its strong and forward-looking regulatory frameworks. Recognized as the region’s most livable city, Abu Dhabi combines a tax-friendly business climate with unmatched connectivity between East and West, alongside world-class healthcare, premier education, and an exceptional lifestyle.
Overview of DIFC and ADGM
DIFC is located in the heart of Dubai, between Downtown Dubai and Emirates Towers, near Sheikh Zayed Road. Dubai is famous for its strategic diversification away from oil, leveraging its strategic location for tourism and global trading, investing in high quality infrastructure, implementing business friendly policies in freezones, and fostering innovation and technology.
While ADGM, located in the capital of the UAE, Abu Dhabi, which is combining abundant oil and gas wealth and a successful diversification strategy that supports non oil-based sectors like manufacturing, finance, construction, and cutting-edge industries such as AI, space, and renewable energy
The DIFC has three independent components: the DIFC Authority, the Dubai Financial Services Authority (DFSA), and the DIFC Courts. While ADGM also has three independent components: the Registration Authority, the Financial Services Regulatory Authority (FSRA), and the ADGM Courts, explained as below:
DIFC (Dubai International Financial Centre)
- DIFC Authority: The body governing the free zone.
- Dubai Financial Services Authority (DFSA): The independent regulator of financial services conducted in or from the DIFC.
- DIFC Courts: An independent English language common law judiciary.
Explore the full details here: DIFC Company Formation Guide 2025 | Setup in Dubai’s Financial Hub
ADGM (Abu Dhabi Global Market)
- ADGM Registration Authority: This authority is responsible for handling the licensing and incorporation procedures in the ADGM company setup.
- Financial Services Regulatory Authority (FSRA):The financial regulatory body of the Abu Dhabi Global Market (ADGM)
- ADGM Courts: An independent judicial system that applies English common law to civil and commercial disputes connected to the ADGM.
Read our Ultimate Guide to ADGM Company Setup for complete insights.
Key Differences Between ADGM and DIFC
Most common types of companies in DIFC are:
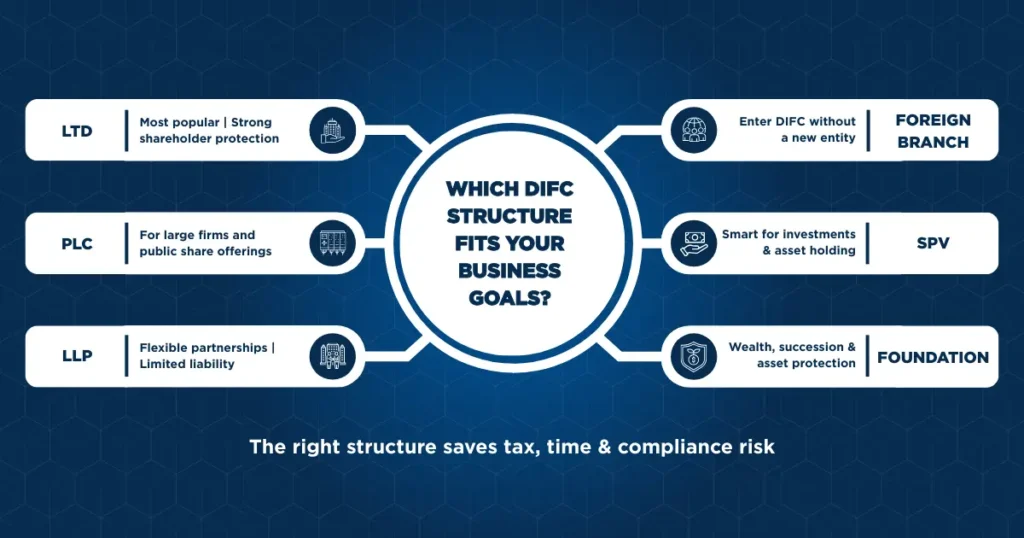
Private Company Limited by Shares (Ltd): Which is considered the most common structure business owners prefer, as it protects shareholders’ interests.
Public Company Limited by Shares (PLC): Large firms often prefer establishing PLCs as it allows them to issue public shares.
Limited Liability Partnership (LLP): Service Providers prefer to issue LLPs as it provides them with the flexibility in addition to protecting partners from each other’s liabilities.
Branch of a Foreign Company: Which is suitable for foreign companies who are interested in operating in DIFC without establishing a totally new legal entity. The branch cannot engage in regulated financial services unless it obtains a separate license.
Special Purpose Vehicle (SPV): Used for securing purposes, asset ownership and liability segregation. SPVs are commonly used for investments and structuring purposes.
Foundation: Used for wealth management, assets protection and succession planning, a Foundation is famous for having its own legal personality separately from the Founder’s.
Discover the complete process, requirements, and tips for foreign investors in our guide:
DIFC Company Formation in 2025: Step-by-Step Guide for Foreign Investors
Most common types of companies in ADGM are:
Public Company Limited by Shares (PLC): A company that can offer it’s shares to the public and must have a capital minimum of USD 50,000.
Private Company Limited by Shares (LTD): A private company that cannot offer its shares to the public and has no minimum capital.
Restricted Scope Company (RSC): Suitable for family offices or entities that are seeking confidentiality and simplified compliance.
Branch of a Foreign Company: This is suitable for companies that want to have a local presence in Abu Dhabi without creating a separate legal entity.
Foundation: Which is used to consolidate holdings of various assets (shares, real property, intellectual property, royalties, etc.) into a single holding entity.
For more detailed info. On the types of companies that are registered with ADGM, you can check our Blog Types of Companies in ADGM .
Setup Costs
Establising a company in DIFC majorly includes DFSA Fees (which are ranging from USD 10,000 For fund management to USD 70,000 for banks), in addition to DIFC Fees that are around USD 20,000 and office space that is charged for USD 80.0 per square feet.
While establishing with ADGM includes FSRA Fees, which can start from USD 5,000 to USD 30,000 per activity, and the office space lease that is charged for USD 80.0 per square feet, also business center option is also available.
Business Activities
Both DIFC and ADGM support a huge range of business activities related to Consultancy, Legal and Accounting Firms, Holding Companies, Family Offices, Fintech and Financial Services. However, the DIFC tends to attract major international financial institutions, whereas the ADGM is more popular among startups and SPV structures due to its simplified regulatory framework and comparatively lower setup and operating costs.
Courts and Dispute Resolution
Both DIFC and ADGM apply the Common Law in a general term. Only DIFC do not directly apply English Common Law as it is, but they mostly follow the Codified Common Law. While ADGM, applies the direct English Law, as is where judgments from English courts are regarded as highly persuasive and, in some cases, effectively binding.
Use Cases and Ideal Business Types
While Both DIFC and ADGM seem to be a good choice for companies that are wishing to set-up whether as start-ups, family businesses, assets management or trading. DIFC as it existed for more than 17 years built an image for finding a trusted freezone with a strong reputation in the region. As DIFC has more that 22,000 professionals in the finance field, and also came up with a robust initiatives such as the FinTech Hive (an accelerator for fintech startups) and the Crowdfunding license (a first for the region).
ADGM, even when it is a new financial centre in the region, is considered a great option for start-ups, specially for it is more-considerate costs and the ongoing adapting environment. ADGM SPV and Foundation regime is considered one of the most flexible regimes in the region. After it’s expanding to Al Reem and Al Maryah Islands, ADGM now is having many requests for setting up Foundations and SPVs.
Choosing between DIFC vs ADGM depends on your business type, cost considerations, and regulatory preferences. Contact Corplex today for expert legal advice to help you make the right choice.
Faqs
-
What is the main difference between DIFC and ADGM?
The main difference between DIFC and ADGM lies in their location, regulatory approach, and target audience. DIFC is based in Dubai and is known for hosting major international financial institutions under a codified common law system, while ADGM is based in Abu Dhabi and applies English common law directly, making it particularly attractive for startups, SPVs, and foundations.
-
Which free zone is better for startups: DIFC or ADGM?
ADGM is generally more suitable for startups due to its lower setup and operating costs, simplified regulatory framework, and flexible structures such as Restricted Scope Companies (RSCs), SPVs, and Foundations. DIFC, on the other hand, is more aligned with established financial institutions and regulated financial activities.
-
What types of companies can be established in DIFC?
Common company types in DIFC include Private Company Limited by Shares (Ltd), Public Company Limited by Shares (PLC), Limited Liability Partnerships (LLPs), Branches of Foreign Companies, Special Purpose Vehicles (SPVs), and Foundations. These structures cater to financial services firms, professional service providers, investment vehicles, and wealth management entities.
-
How do DIFC and ADGM differ in terms of regulatory authorities and courts?
DIFC is regulated by the Dubai Financial Services Authority (DFSA) and has its own DIFC Courts operating under a codified common law system. ADGM is regulated by the Financial Services Regulatory Authority (FSRA) and applies English common law directly through ADGM Courts, where English court judgments are highly persuasive.
-
Which is more cost-effective: setting up a company in DIFC or ADGM?
ADGM is generally more cost-effective, with regulatory fees starting from around USD 5,000 and flexible office solutions available. DIFC setup costs are higher due to DFSA regulatory fees, DIFC authority fees, and premium office space requirements, making it more suitable for larger or regulated financial entities.

